James Little, Checkered Past, 2017. Courtesy of Kavi Gupta.
With the pandemic-induced upheaval of 2020 and 2021, the art market in 2022 was in some ways a return to routine, but in others, unprecedented.
The first half of the year was still consumed with NFTs and the potential for web3, while at the same time a frothy market bubbled up around emerging talents’ works, leading to splashy debuts and ample auction records. And while the second half of the year saw the market soften, or perhaps, correct itself, interest in the ultra-contemporary market was strong this fall, not just at auctions but at galleries, too, with plenty of relative newcomers joining the rosters of major galleries.
As notable women artists, both emerging and established, earned due acclaim, both critically and commercially, so, too, did the genre of abstraction. And though exceptional and viral moments like the Paul Allen sale and MSCHF’s ATM may account for the key moments when art infiltrated mainstream culture this year, the true market trends of 2022 were far more representative of what’s relevant to artists, collectors, and art world professionals, and indicative of what we can expect heading into 2023.
1. NFTs rise and fall

Larva Labs, CryptoPunk #4596, 2017. Yuga Labs, Bored Ape Yacht Club #197, 2021. Courtesy of Asia Art Center.
At the beginning of 2022, NFTs seemed to be on track to take over the world. In March, Bored Ape Yacht Club founders Yuga Labs acquired CryptoPunks and Meebits, creating an NFT behemoth, while many NFT artists used profits of their work to benefit war efforts in Ukraine. Decentralized crowdfunding of artworks took off: In February, Pak’s Clock sold to a group of collectors organized through a DAO, for a record $53 million in Ethereum (the proceeds went to benefit Julian Assange’s legal fund).
Meanwhile, plenty of galleries moved to cater to this new segment of collectors. With crypto-wallets overflowing, the question was how to involve collectors in the rest of the art market, especially after tech billionaire Justin Sun’s purchase of Alberto Giacometti’s Le Nez (Nose) (conceived 1947/49; cast 1965) at Sotheby’s for $78.4 million in late 2021.
Yet by May, much of the shine of blockchain-based works was depleted by the enormous crash in the prices of cryptocurrencies, which only deepened as the year went on, due in part to the implosion of cryptocurrency exchange FTX. While there’s much talk of “crypto contagion,” the art world continues to find ways to work with NFTs.
Christie’s, for example, announced its sparkling new platform, Christie’s 3.0, to coincide with Miami Art Week (the event that, in 2021, was abuzz with newly minted crypto-wealthy collectors). In 2023, it’s hard to see crypto being as hyped as it was in 2021, but without the astronomical prices and buzz, who knows what the next phase of NFT art might look like?
2. Collecting with a purpose
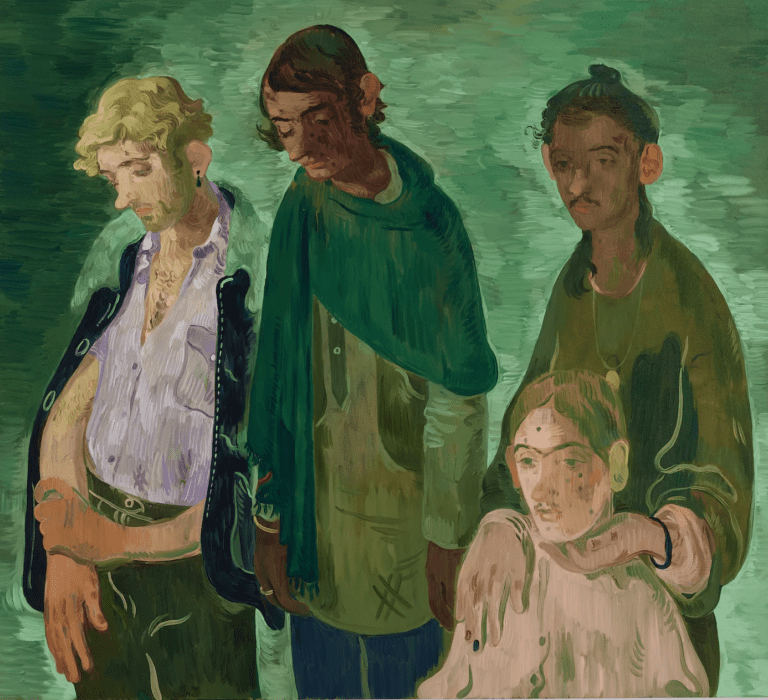

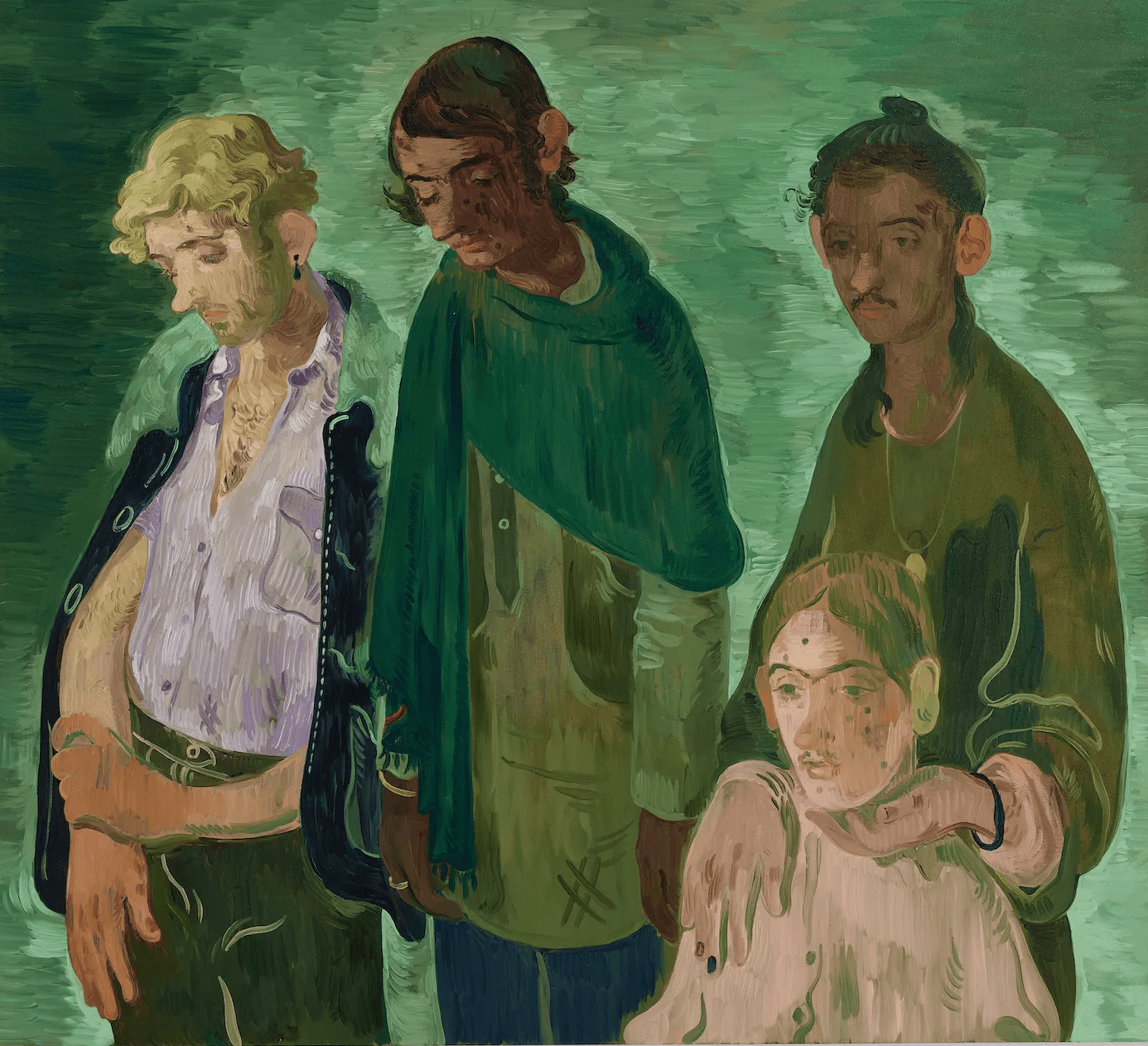
Salman Toor, 4 Guests, 2019. Courtesy of the artist and Christie’s Images Limited.
Depicting four downcast figures against a background of his signature pea green, Salman Toor’s 4 Guests (2019) was one of the standout lots in Christie’s 21st-century evening sale that took place on November 17th. At $856,800, it went for nearly four times its estimate—which is easy to cheer, since the work was donated by Toor to benefit a charity working with emergency flood relief efforts in Pakistan. It was hardly the only sale of its kind this year. The month prior, Stanley Whitney and Gagosian sold one of the artist’s signature abstract canvases via Artsy Auctions in support of the Art for Justice Fund and Planned Parenthood of Greater New York.
In February and March, art institutions, artists, and auction houses acted quickly to step up in support of Ukraine, recognizing the severity of the crisis. While these commitments to a wider purpose are still a fraction of the art market’s economic activity, the speed and force with which art world players took action indicated a commitment to concretely acknowledge the issues that are important to its audience.
These benefit auctions, after all, coincide with a growing number of collectors focusing their purchases around marginalized communities, like BIPOC, women, or LGBTQ+ artists. More collectors are prioritizing sustainability when purchasing art, too. According to the Art Basel and UBS report “The Art Market 2022,” a majority of collectors said they have focused on reducing their carbon footprint by traveling to fewer fairs, and are opting for more sustainable shipping methods. The art world is slow to change, but it’s refreshing to see more conversations about art’s impact on the world around it.
3. Abstraction ascends

Jadé Fadojutimi, There exists a glorious world. Its name? The Land of Sustainable Burdens, 2020. Courtesy of Pippy Houldsworth Gallery.
Was it a pandemic-induced need to see people, things, and environments again? Or were portraits just on trend? Either way, in 2021, figuration was everywhere. Faces, objects, and recognizable scenes peeked out of art fair booths, galleries’ online viewing rooms, and auction catalogues. This year, however, the tide seems to be shifting.
At Gagosian’s Frieze London fair booth, for instance, abstract painter Jadé Fadojutimi’s works, each priced at £500,000 ($614,000), were sold out before the fair even opened. And at a Phillips sale in Hong Kong in early December, Lucy Bull set a new record at her Asian auction debut: Her work 8:50 (2020) sold for HK$11.4 million (US$1.5 million).
It’s not only younger artists. This year also saw critically acclaimed exhibitions for Bernice Bing, an underrecognized Abstract Expressionist artist; and James Little, who is becoming increasingly known for his geometric, monochromatic forms. It seems, even in uncertain times, some trend cycles will always roll back and forth.
4. Young artists reach new heights

Flora Yukhnovich Warm, Wet N' Wild, 2020. Courtesy of Parafin. Louise Giovanelli, Consumer, 2022. Courtesy of White Cube.
Earlier this year, Rococo-influenced painter Flora Yukhnovich, born in 1990 and represented by Victoria Miro since 2021, set a gargantuan new sales record: $3.1 million at auction. Never was it more clear that the ultra-contemporary market is booming.
At auction, young artists are reaching prices that would have been unheard of at the start of this century, and with a surprising frequency. Sotheby’s launched a new marquee sale in New York in November 2021 called “The Now,” the first evening sale devoted solely to this category. Earlier this year, a survey by Artprice focused on auction results for works by artists under 40 showed that the ultra-contemporary art market generated $420 million between July 2021 and June 2022—a 28% increase on the previous year. This is due to both the value and volume of these works at auction increasing in 2022.
On the buyer side, meanwhile, there seems to be no limit to the amounts that keen collectors will pay, with gallery waitlists apparently filling up into the hundreds. That’s why, even with the spiraling prices, works by young artists are also competitive. The sell-through rate for ultra-contemporary artworks at auction is around, or even higher than, the rest of the market.
Even though the auction houses are where this trend is most visible, it seems to have affected almost every aspect of the art world, with blue-chip galleries, too, leaning into the frenzy. White Cube, for instance, started representing Danica Lundy (born 1991), Louise Giovanelli (born 1993), Ilana Savdie, and Marguerite Humeau (both born 1986) this year. Gagosian, meanwhile, picked up painters Jadé Fadojutimi (born 1993) and Anna Weyant (born 1995); the latter artist’s skyrocketing prices in particular have caused quite a stir.
5. Surrealism surges
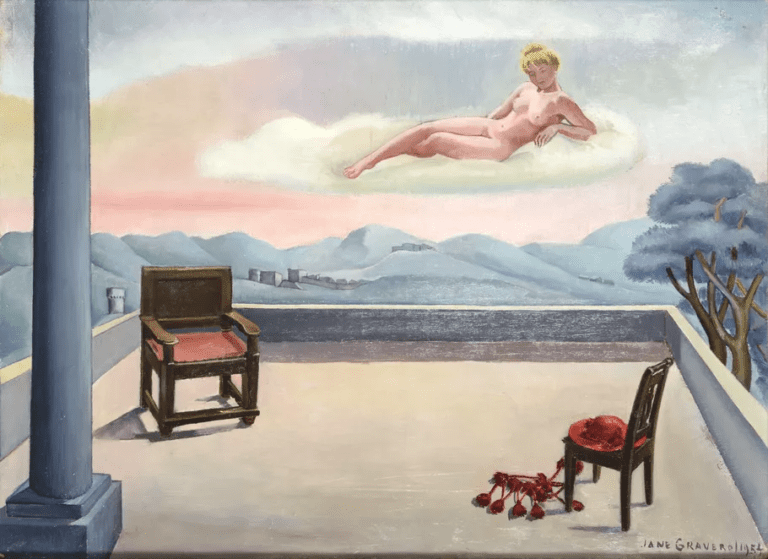
Jane Graverol, Le Démon Mesquin, 1952. Courtesy of DIGARD AUCTION.
Although “Surrealism Beyond Borders” opened late last year at the Met, its impact echoed throughout this year, as the cross-generational, international exhibition moved on to Tate Modern, offering a reconsideration of the movement and its less well-known proponents. By the time the Venice Biennale opened in April, the frenzy for Surrealist and contemporary surrealistic works had hit new heights.
In Venice, curator Cecilia Alemani’s “The Milk of Dreams” exhibition foregrounded the subconscious, the mythical, and the spectral through a female-led list of Surrealists like Jane Graverol, Unica Zürn, and Alice Rahon, alongside contemporary artists like Dora Budor, Marianna Simnett, and Raphaela Vogel, who explore those themes in new ways.
None of this passed the auction houses by: Both Sotheby’s and Christie’s presented sales (noticeably far more male-heavy than the Venice show) organized around the movement. As sales of works by female Surrealists like Dorothea Tanning and Leonora Carrington continue to exceed estimates, particularly smaller works and prints, these dream-influenced artists still prove to be popular with collectors.